Plate heat exchangers are compact equipment that provide efficient heat transfer between two fluids. They have been widely used for many years due to their ability to meet critical requirements such as energy savings, process safety, and space efficiency in the industry. As one of Turkey's first domestic plate heat exchanger manufacturers, we continue to offer these devices under the MIT brand, tailored to the needs of different sectors with our technologies developed over approximately 20 years.
Plate exchangers allow hot and cold fluids to exchange heat without mixing through narrow channels formed by thin metal plates. The high turbulence flow structure increases heat transfer efficiency, while the compact design provides significant advantages in terms of both hygiene and energy savings for businesses. This general structure is a key factor that expands the usage area of plate exchangers from air conditioning to energy production, from chemical processes to the metal industry.
Stainless steel plate exchangers are a special version of this technology optimized for applications that require hygiene. Used in food processes, beverage production, milk pasteurization, and pharmaceutical applications, this equipment plays a critical role in maintaining surface hygiene and preventing bacterial growth. The high corrosion resistance of stainless steel, the safety offered by hygienic design, and the suitable surface structure for regular cleaning make these exchangers indispensable in sensitive processes.
The purpose of this blog post is to compare standard plate heat exchangers with stainless steel plate exchangers from a technical, economic, and application-based perspective; to provide a clear framework on which type should be preferred in which sectors. Thus, businesses can increase their efficiency by selecting the most suitable heat exchanger solution for their processes and achieve a more sustainable operational structure.
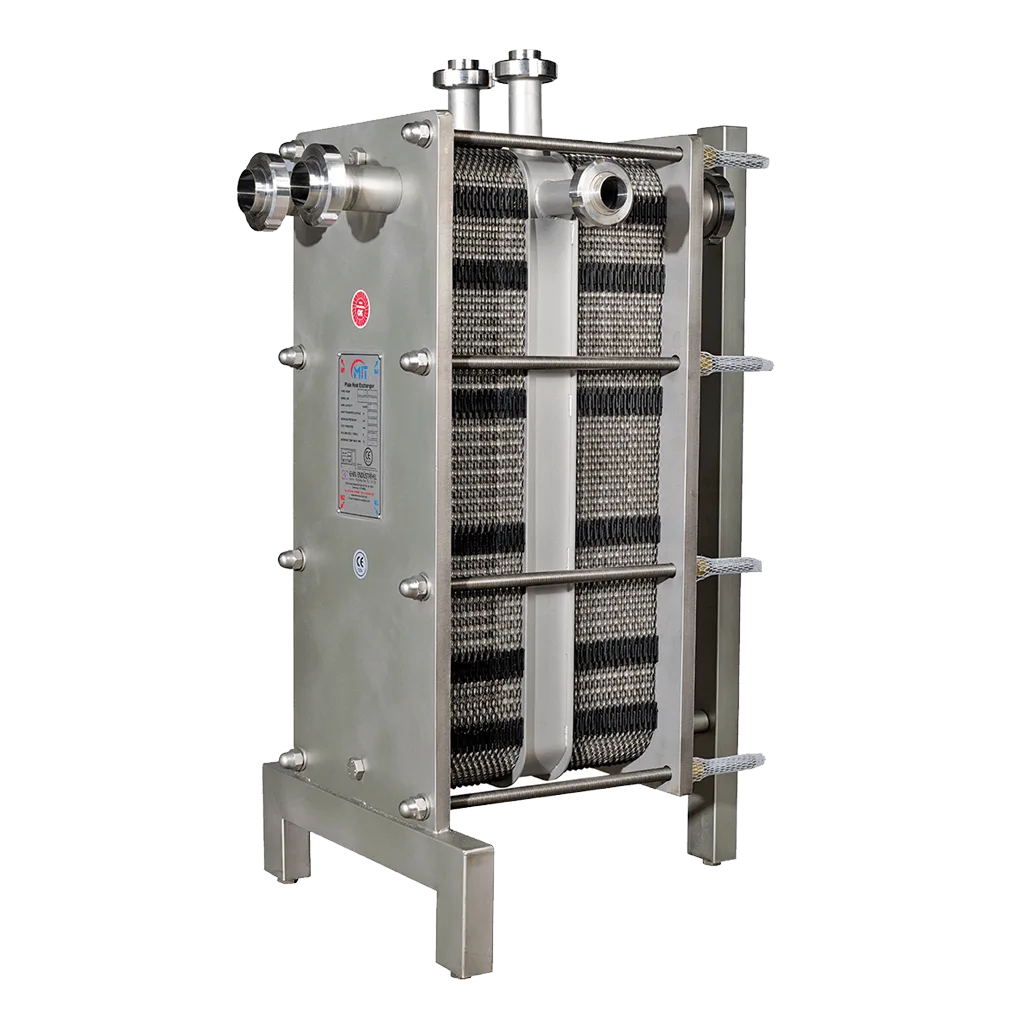

Plate heat exchangers are compact heat transfer equipment consisting of narrow flow channels formed by thin metal plates arranged parallel to each other. The special geometry on these plates allows the fluid to create turbulence in a controlled manner. Thus, both the heat transfer coefficient increases and high performance is achieved by minimizing the total size of the exchanger.
The plates that form the basic structure are usually made of stainless steel, titanium, or nickel alloys. These materials are ideal for industrial applications due to their thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion. The plates are isolated from each other by gaskets or welded structures, and each fluid progresses in its channel, exchanging heat without mixing with the other fluid.
The operating principle is based on directing hot and cold fluids in a counterflow or crossflow arrangement between the plates. The counterflow structure provides more efficient heat transfer by maximizing the temperature difference. The wavy or embossed surface of the plates increases the fluid's contact with the surface while controlling flow rate and turbulence, accelerating heat transfer.
One of the most important features of plate heat exchangers is their modular structure. Capacity can be increased or decreased by adding or removing plates. This flexibility allows for quick adaptation to different process needs. Additionally, the ability to disassemble and reassemble the plates facilitates cleaning and maintenance operations, reducing operating costs.
Sealing, which is critical for process safety in industrial facilities, is achieved with special materials used in gasketed structures. This design also reduces sediment accumulation and supports a more homogeneous distribution of fluids. As a result, plate heat exchangers have become a preferred solution in many sectors by offering both high energy efficiency and long-lasting use.
Outstanding Features of Stainless Steel Plate Heat Exchangers
Stainless steel plate heat exchangers are specially designed heat exchangers used in sectors where hygiene and process safety are critically important. Although they operate on the same principle as standard plate exchangers, they offer a safer and more durable solution for food, beverage, pharmaceutical, and chemical production processes due to the materials used and surface structure.
The most significant difference of these exchangers is that all wet surfaces are made of high-quality stainless steel. The corrosion resistance of stainless steel ensures long-lasting and reliable use, especially in facilities working with sensitive products such as milk, fruit juice, beer, whey, and similar items. The smooth surface structure of the material reduces bacterial retention and contributes to maintaining hygiene standards by facilitating cleaning processes.
The plates used in stainless steel exchangers have special geometries that create high turbulence. This geometry allows the fluid to make full contact with the plate surface, enabling the product to be heated or cooled uniformly. Especially in processes where temperature control is critical, such as pasteurization, this turbulence and homogeneous flow are of great importance for preserving product quality.
Another critical advantage is ease of cleaning and maintenance. The chemical resistance of stainless steel allows for compatibility with automated cleaning processes performed with CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems. This accelerates cleaning operations on production lines, reduces downtime, and ensures process continuity.
Stainless steel plate exchangers also offer higher stability in facilities processing aggressive fluids or products with high acidity levels. Resistance to corrosion extends the equipment's lifespan while minimizing the risk of surface damage or contamination that may occur during the process.
All these features make stainless steel plate exchangers a high-performance solution that is safely used not only in hygiene-focused sectors such as food and pharmaceuticals but also in chemical, beverage, and industrial processes.
Comparison of Both Exchanger Types
Although plate heat exchangers and stainless steel plate heat exchangers operate on fundamentally the same principles, they show significant differences in terms of usage purpose, material structure, hygiene requirements, and durability levels. The evaluations below provide a technical comparison that will help businesses choose the right equipment suitable for their needs.
Heat Transfer Efficiency
Standard plate heat exchangers offer quite high efficiency thanks to the large heat transfer surface provided by thin metal plates and the turbulent flow structure. Stainless steel exchangers also have similar thermal performance; however, due to their hygienic surface structure, some models can have more controlled plate geometry. Generally, both types provide high heat transfer coefficients; the difference mostly arises according to application requirements.
Hygiene and Food Safety
Hygiene criteria create the most distinct distinction between the two types of equipment.
While standard plate exchangers are sufficient for many industrial processes, in the food and beverage sectors, stainless steel plate exchangers are preferred due to their smooth surface and bacteria-repellent structure. The chemical resistance of stainless steel maintains surface stability in processes where cleaning chemicals are used intensively. Therefore, stainless alternatives become mandatory in pasteurization and sterile production lines.
Suitability for Application Areas
Standard plate exchangers can be used in a wide range of applications such as HVAC, energy, metal processing, automotive, petrochemical, textile, and marine.
Stainless steel plate exchangers, on the other hand, are specifically developed for:
• Milk pasteurization
• Juice cooling
• Beverage production
• Hygienic process lines
• Chemically aggressive environments
for more specific and sensitive applications.
Thermal Performance Flexibility
Both types of exchangers allow for capacity changes by increasing the number of plates thanks to their modular designs.
However, in stainless steel models, since plate thickness, surface structure, and gasket material are optimized for food-focused processes, thermal design is often specifically shaped for applications requiring precise temperature control. This situation enhances process quality while minimizing energy losses.
Process Safety and Sealing Level
Standard plate models are resistant to high pressure and temperature conditions, but wear on gaskets can be observed with long-term use.
In stainless steel plate exchangers, both the gaskets and plate surfaces have better chemical resistance. This durability provides extra safety, especially in applications where the risk of product contamination exists.
Advantages of Plate Exchangers and Industrial Application Areas
Plate exchangers are a type of heat exchanger preferred in many industries due to their compact structures, high heat transfer efficiencies, and flexible design features. Their modular structures and optimized hydrodynamic designs help businesses reduce operational costs and increase process safety. These features make plate exchangers an ideal solution for both new installations and modernization projects in existing facilities.
One of the most significant advantages of plate exchangers is their high thermal performance due to the large heat transfer surface. The wavy or embossed structure of the plates ensures full contact of the fluid with the plate surface and increases turbulence. Thus, heat exchange occurs quickly and efficiently. They also occupy significantly less space compared to traditional tubular exchangers, providing space savings in facilities.
Another important advantage is the flexibility of modular design. Capacity can easily be changed by increasing or decreasing the number of plates. This feature allows for adaptation to different flow and temperature needs. Additionally, the ability to disassemble and clean the plates during maintenance supports operational continuity and the longevity of the equipment.
Plate exchangers prevent efficiency losses that may occur in the system due to their flow structure that reduces sediment accumulation. Furthermore, the flow arrangement inside the exchanger provides protection against sudden pressure increases in the installation, enhancing process safety. Models with wide channels offer more durable solutions in fluids containing solid particles, while semi-welded and welded models are more resilient in aggressive chemical environments.
These technical advantages have ensured the widespread use of plate exchangers in many sectors.
The main industrial application areas are as follows:
Climate Control and HVAC Systems: Provides high-efficiency heat transfer in heating-cooling circuits, heat pumps, and cooling towers.
Food and Beverage Industry: Offers reliable temperature control in milk cooling, juice heating-cooling, beer production, and various pasteurization processes.
Energy and Cogeneration Systems: Used in applications such as waste heat recovery, steam condensation, and engine cooling.
Petrochemical and Pharmaceutical Industry: Provides durable and stable performance in heating and cooling processes of various chemicals.
Metal and Textile Industry: Increases process efficiency in production lines requiring temperature control.
Marine: Safely serves in ship cooling and heating systems thanks to its saltwater-resistant solutions.
With all these advantages, plate heat exchangers are among the indispensable equipment of modern industrial facilities in terms of energy efficiency, process safety, and optimization of operating costs.
Advantages of Stainless Steel Plate Exchangers and Their Role in the Food Industry
Stainless steel plate heat exchangers are designed to provide reliable, durable, and long-lasting solutions in processes with high hygiene requirements. These exchangers are widely used in the food and beverage industry due to the corrosion resistance of stainless steel, smooth surface structure, and suitability for cleaning processes. In all applications where product safety and process quality are priorities, stainless steel plate exchangers offer advantages that differentiate them from standard models.
The most important advantage of this equipment is its compliance with high hygiene standards. The non-corrosive structure of stainless steel reduces the formation of residues on the surface and allows for easy cleaning of areas in contact with the product. Their compatibility with CIP (Clean-in-Place) cleaning systems shortens cleaning times on production lines while minimizing contamination risks. This feature is especially vital for sensitive products such as milk and dairy products.
Stainless steel plate heat exchangers demonstrate long-lasting performance in processing acidic, salty, or chemically aggressive products thanks to their high corrosion resistance. They provide stable results in terms of both heat transfer and surface durability in products such as fruit juice, brine, beer, and whey. This durability significantly extends the equipment's lifespan while reducing maintenance costs.
Another important advantage of these exchangers is their ability to provide high homogeneity in heating and cooling. The wavy surface of the plates ensures that the fluid is evenly distributed along the plate, allowing the product to be processed at the ideal temperature. In processes where temperature sensitivity is critical, such as pasteurization, they play an effective role in maintaining product quality and microbiological safety.
The main areas of use in the food industry are as follows:
• Milk pasteurization
• Cream pasteurization
• Whey processes
• Fruit juice heating-cooling
• Beer production and pre-fermentation cooling
• All processing lines requiring hygienic heat exchange
In these sectors, process continuity, hygiene, safety, and product quality are prioritized, making stainless steel plate heat exchangers a much more effective alternative compared to standard exchangers.
As a result, stainless steel plate heat exchangers are indispensable equipment in modern food production facilities due to their critical advantages such as durability, hygiene, heat transfer efficiency, and easy maintenance.
Which Exchanger Should Be Preferred in Which Situation?
Although plate heat exchangers and stainless steel plate heat exchangers have similar operating principles, application requirements and process conditions directly affect the choice. Determining the correct type of exchanger is a critical decision that directly impacts product quality, energy efficiency, operating costs, and equipment lifespan. Therefore, the advantages of both types of exchangers should be evaluated alongside the required process characteristics.
Standard plate heat exchangers are ideal solutions for applications that require high efficiency but do not have a hygienic environment requirement. They have a wide range of applications in HVAC systems, industrial cooling lines, energy recovery applications, metal processing processes, and chemical heating-cooling systems. Thanks to their modular structures, it is easy to increase capacity as the facility grows, and overall maintenance costs are low. Therefore, they provide advantages in terms of both investment costs and operational ease.
Stainless steel plate exchangers should be preferred in applications where hygiene, product quality, and corrosion resistance are priorities. Surface hygiene is critical during the heating or cooling of sensitive products such as milk, fruit juice, cream, beer, and others in the food and beverage industries. The chemical resistance of stainless steel, its compatibility with CIP cleaning systems, and its smooth surface reduce contamination risks and guarantee product safety. Additionally, they provide longer-lasting use in acidic or salty environments.
If the process requires high temperature sensitivity or if product quality is directly dependent on the homogeneity of heat transfer, stainless steel models are a more accurate choice. Conversely, if the process environment contains aggressive chemicals, if temperature fluctuations occur frequently, or if stable performance is expected in long-term operations, stainless solutions will again be more reliable.
In summary:
• General industrial applications, HVAC, energy recovery, chemical processes: Standard plate exchanger
• Food, beverage, pharmaceutical, hygienic production lines, processes exposed to corrosion: Stainless steel plate exchanger
Both types of exchangers provide high efficiency; however, the correct choice ensures long-term optimization in terms of process safety, product quality, and operating costs.
Evaluation in Terms of Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Plate heat exchangers and stainless steel plate heat exchangers are widely used systems aimed at increasing energy efficiency in industrial facilities and supporting sustainable production processes. Both types of equipment make significant contributions to recovering waste heat, reducing energy loss in processes, and lowering operating costs. These features play a critical role in meeting sustainable production goals in today's industrial applications.
Plate exchangers provide high heat transfer with low energy consumption thanks to their large heat transfer surface and optimized flow channels. This design allows businesses to achieve the same process efficiency with less energy consumption. They offer significant advantages, especially in energy recovery applications in HVAC systems, cogeneration lines, and cooling circuits. The high turbulent flow structure increases the heat transfer coefficient, allowing for effective heat exchange with lower temperature differences. This situation reduces energy usage while enhancing process performance.
Stainless steel plate exchangers offer a more advanced solution in terms of energy efficiency, product safety, and process sustainability. Thanks to their hygienic surface structure, cleaning costs and energy consumption are optimized in sensitive sectors such as food and beverage. Their compatibility with CIP systems ensures that cleaning processes are completed in a shorter time and that sustainable production standards are met with less chemical use. Additionally, the corrosion resistance of stainless steel extends the equipment's lifespan, reducing resource consumption in the long term.
From the perspective of energy efficiency, both types of exchangers provide advantages in terms of low operating costs, long-term use, and reducing environmental impact. However, when evaluated with a focus on sustainability, stainless steel plate exchangers take environmental performance a step further with their lower maintenance needs, reduced cleaning chemical consumption, and structure that preserves product safety. Both types of exchangers are among the key components of modern process optimization in line with industries' goals to reduce their carbon footprint.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Exchanger According to Application
Plate heat exchangers and stainless steel plate heat exchangers are critical equipment that offer high efficiency, energy savings, and reliable performance in industrial processes. However, each type of exchanger responds to different needs in terms of material properties, hygiene criteria, and process durability. Therefore, the right exchanger selection should be made not only according to technical requirements but also in accordance with the operational standards of the industry and product safety expectations.
Standard plate heat exchangers provide high performance and an economical solution in HVAC, energy, chemical, metal, and general industrial applications. Due to flexible capacity management, low maintenance costs, and compact design advantages, they become an ideal choice for many facilities. These exchangers provide fast, efficient, and sustainable heat transfer in processes where hygiene requirements are not present.
Stainless steel plate exchangers, on the other hand, are indispensable, especially in sectors where hygiene is a priority, such as food, beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. The corrosion resistance of stainless steel, its smooth surface structure, and compatibility with cleaning processes make these exchangers reliable for processing sensitive products. In all applications where surfaces in contact with the product must remain sterile, stainless steel models provide much higher safety and quality compared to standard exchangers.
In conclusion, both types of exchangers have strong advantages in their respective fields. For optimal selection, process temperature, fluid properties, hygiene requirements, chemical resistance expectations, and the business's energy efficiency goals should be evaluated together. A well-chosen exchanger not only increases production efficiency but also supports long-term operational sustainability and elevates process safety to the highest level.